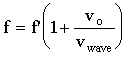 .
.Physics of Music - Review Sheet #2
Anything marked with a * will be given as information on the exam.
Perception of beats:
Two pure tones at f1 and f2: if |f1 - f2| is:
Less than 10 Hz - hear an average pitch of 1/2(f1 + f2) and beats.
Greater than 15 Hz - Critical bandwidths overlapping. Hear one tone but dissonant. 30-40 Hz the worst.
Greater than half step - hear two distinct tones, but still dissonant.
Greater than Critical Bandwith - hear two distinct and consonant tones. Also a difference tone.
Consonance/Dissonance -if beats occur in the range of 10 - 50 Hz for the fundamental or any harmonics, the two notes sound dissonant.
Doppler shift:
Role of medium - Doppler shift occurs when there is motion with respect to the medium.
Moving observer - a moving observer will detect a shifted frequency given by:
*
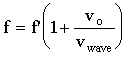 .
.
Moving source - a moving source will produce a shifted frequency given by:
*
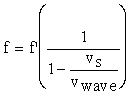 .
.
Double Doppler Shift - If both source and observer are moving, first find the Doppler shifted frequency for an observer at rest in the medium. Then this observer bcomes a stationary source for the next part.
Reflection - a reflected wave acts like it is produced by the reflecting surface.
Source exceeding the wave speed:
Sonic boom - source traveling faster than the speed of sound.
Cherenkov radiation - source traveling faster than the speed of light.
Wake of a boat - source traveling faster than the speed of water waves.
Mach Cone - the shock wave forms a cone. The angle of the cone is given by
*sin(q) = vwave/vsource
Gain and feedback:
Gain - increase in the amplitude of a wave due to amplification.
Overall gain - overall increase or decrease in a wave due to amplification or loss.
Feedback - occurs when a loop exists between the source of a wave and the detection of a wave and the overall gain exceeds one.
Cavity feedback - occurs at resonant frequencies of a cavity for which the overall gain exceeds one.
Cavity diagrams:
A plot of the resonant frequencies of a cavity as a function of some variable that is being changed.
Light waves:
Medium - not well understood.
Speed - speed of light = c = 3× 108 meter/second.
Doppler shift at low speeds - just like other waves.
Interference effects:
Steps - reflection off of steps produces a tone. Can get constructive and destructive interference.
Thin films - reflection off of thin films can lead to constructive or destructive interference.
Hearing:
Parts of the ear - ear canal, ear drum, small bones, oval window, cochlea.
Critical bandwidth - range of frequencies that respond to a given pitch. The CB is equal to 19% of the frequency unless the frequency is 500 Hz. Below 500 Hz the CB is always 90-95 Hz.
Just noticeable difference - smallest interval that can be heard. The JND is equal to 0.5% of the frequency.
Pure tones - contain no overtones.
Complex tones - contain some amount of overtones, gives tone quality or timbre.
Consonance/dissonance of complex tones - must compare the overtones with each other.
"Missing fundamental" - pitch of a complex tone given by the fundamental frequency, even if that frequency is not present in the tone.